The PFAS allows abbreviations to be used in emsCharts to make typing less painful.
To ensure that medical abbreviations are unambiguous, abbreviations that appear anywhere in the EMS Field Guide 2007 Sixth Edition, Basic & Intermediate or are already used in the emsCharts software may be used. Other medical abbreviations will not be accepted unless you indicate what you mean by the abbreviation somewhere in the chart.
If you have a need to repeatedly use an abbreviation in a chart, spell it out once and put YOUR abbreviation in parentheses immediately following the term. For example:
My Special Abbreviation (MSA)
The table below includes all the abbreviations I believe are included in the Field Guide and emsCharts. If I missed any, let me know. If I have made any errors, let me know.
There are some abbreviations in the Field Guide that are not in my list because they involve special characters or fonts that are not easy to insert into emsCharts. These are symbols like
α, β, Δ, 1°, 2°, 3°,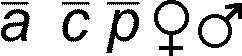
Such special characters may be embedded in a chart if it is absolutely essential, but this practice is strongly discouraged. If you must embed special characters or formatting, contact the software administrator.
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| > | greater than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| @ | at |
| AAO | alert and oriented |
| a.c. | before meals |
| ABC (ABCs) | airway, breathing, circulation |
| ABCDE | airway, breathing, circulation, disability, expose |
| abd | abdomen |
| ABG | arterial blood gas |
| abn | abnormal |
| ACLS | advanced cardiac life support |
| ADHD | Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder |
| Adm. | administration |
| AED | automated external defibrillator |
| AEIOU | alcohol/drugs, endocrine, insulin/infection, overdose, uremia |
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| AIDS | acquired immunodeficiency syndrome |
| AKA | also known as |
| ALS | advanced life support |
| AMA | against medical advice |
| AMI | acute myocardial infarction |
| ANS | autonomic nervous system |
| ant. | anterior |
| AODM | adult-onset diabetes mellitus |
| A-P, AP | anterior-posterior |
| APAP | acetaminophen |
| APGAR | appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, respirations |
| APE | acute pulmonary edema |
| ARC | AIDS-related complex |
| asa | acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) |
| ASAP | as soon as possible |
| ASHD | arteriosclerotic heart disease |
| ausc | auscultation |
| A-V | arteriovenous, atrioventricular |
| AVPU | alert, responds to verbal, responds to pain, unresponsive |
| ax | axillary |
| BBB | bundle branch block |
| b.i.d. | twice a day |
| bilat | bilateral |
| Bl s | blood sugar |
| BLS | basic life support |
| BM | bowel movement |
| BP, B.P. | blood pressure |
| BS | breath sounds |
| BSA | body surface area |
| BSI | body substance isolation |
| BVM | bag-valve-mask |
| C | centigrade |
| CA | cancer |
| CABG | coronary artery bypass graft |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CAO | conscious, alert, oriented |
| CAT | computerized axial tomography |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| CC | chief complaint |
| cc | cubic centimeter |
| CCU | coronary care unit |
| CHF | congestive heart failure |
| CID | cervical immobilization device (blocks) |
| CISD | critical incident stress debriefing |
| Cl | chloride |
| cm | centimeter |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| c/o | complaining of |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| COHb | carboxyhemoglobin |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CPR | cardio pulmonary resuscitation |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| C-spine | cervical spine |
| CVA | cerebrovascular accident (stroke) |
| cx | chest |
| D5W | Dextrose 5% in Water |
| D/C | discontinue |
| Decon | decontamination |
| dl | deciliter (100 ml) |
| DKA | diabetic ketoacidosis |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| DNR | do not resuscitate |
| DOA | dead on arrival |
| DOE | dyspnea on exertion |
| DSD | dry sterile dressing |
| DTR | deep tendon reflex |
| DT's | delirium tremens |
| Dx | diagnosis |
| EBL | estimated blood loss |
| EEG | electroencephalogram |
| EENT | eyes, ears, nose, and throat |
| ED | emergency department |
| EKG | electrocardiogram |
| EMS | emergency medical service |
| EMT | emergency medical technician |
| ENT | ears, nose & throat |
| EPS | extrapyramidal sympt. (dystonias) |
| ET | endotracheal |
| ETOH | ethyl alcohol |
| F | Fahrenheit |
| FH | family history |
| FHR | fetal heart rate |
| FUO | fever of undetermined origin |
| fv | fever |
| Fx | fracture |
| g, Gm | gram |
| GCS | Coma Score |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| gr | grain |
| GSW | gun shot wound |
| gt | drop |
| gtt | drops |
| GU | genitourinary |
| GYN | gynecology |
| H+ | hydrogen ion |
| h. | hour |
| Hb, Hgb | hemoglobin |
| HBP | high blood pressure |
| H&P | history and physical examination |
| H/A | headache |
| HazMat | hazardous materials (team) |
| HCO3 | bicarbonate ion |
| Hct | hematocrit |
| HEENT | head, eyes, ears, nose, and throat |
| Hg | mercury |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| H2O | water |
| HPI | history of present illness |
| HR, H.R. | heart rate |
| HTN | hypertension |
| hx, HX | history |
| ICP | intracranial pressure |
| ICS, IS | intercostal space |
| IDDM | insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| IL | intralingual |
| IM | intramuscular |
| I&O | intake and output |
| IO | intraosseous |
| IPPB | intermittent positive pressure breathing |
| IRR | irregular |
| IU | International units |
| IUD | intrauterine device |
| IV | intravenous |
| IVP | intravenous push; intravenous pyelogram |
| JVD | jugular venous distension |
| K+ | potassium ion |
| KED | Kendrick extrication device |
| kg | kilogram (1000 grams; 2.2 pounds) |
| KVO | keep vein open (30 - 60 µgtt/min) |
| L | left |
| L | liter |
| LA | left arm |
| lb | pound |
| LL | left leg |
| LLB | long board |
| LLQ | left lower quadrant |
| LMP | last menstrual period |
| LOC, L.O.C. | level of consciousness |
| LP | lumbar puncture |
| LPM, L/m, l/min, L/MIN | liters per minute |
| LS | lung sounds |
| LUQ | left upper quadrant |
| Lv | leave |
| LZ | landing Zone |
| Mast | military antishock trousers |
| mcg | microgram (1 (µg)1,000,000 of 1 gram) |
| mEQ | milliequivalent |
| Mg++ | magnesium ion |
| mg | milligram (1/1,000 of 1 gram) |
| MI | myocardial infarction |
| m | meter |
| ml, mL | milliliter (1/1,000 of 1 liter; 1 cc) |
| mm | millimeter |
| MOI | mechanism of injury |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| MVA | motor vehicle accident |
| Na+ | sodium ion |
| NA, N/A | not applicable |
| NaCl | sodium chloride |
| NAD | no acute distress, no apparent distress |
| NaHCO3 | sodium bicarbonate |
| NB | newborn |
| NG | nasogastric |
| NIDDM | non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus |
| NKA | no known allergy |
| NPO | nothing by mouth |
| NRB | non-rebreather (mask) |
| NS | normal saline (0.9%) |
| NSAID | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug |
| NS | normal saline |
| NSR | normal sinus rhythm |
| NTG | nitroglycerin |
| N&V | nausea and vomiting |
| O2 | oxygen |
| OB | obstetrics |
| OD | overdose |
| OD | right eye |
| OLMC | On-line Medical Control |
| OPQRST | onset, provoke/palliative, quality, region or radiation, signs/symptoms/severity, time of onset/duration/intensity |
| OS | left eye |
| oz | ounce |
| PAC | premature atrial contraction |
| PASG | pneumatic antishock garment |
| PAT | paroxysmal atrial tachycardia |
| PCO2 | carbon dioxide pressure |
| p.c. | after meals |
| PE | physical exam |
| PEA | pulseless electrical activity |
| PEARL, PERL | pupils equal and react to light |
| PEEP | positive end-expiratory pressure |
| pH | hydrogen ion concentration (inverse) |
| PID | pelvic inflammatory disease |
| PJC | premature junctional complex |
| PLA | Plasmalyte-A |
| PMH | past medical history |
| PND | paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea |
| P.O., p.o.,PO | by mouth, orally |
| PO2 | oxygen pressure |
| PP | postpartum |
| pr | per rectum; rectally |
| PRN, p.r.n. | as needed |
| PSM | pulse, sensory & motor functions |
| PSVT | paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia |
| Pt., pt, (pts), Pt | patient (patient's, patients) |
| PTA | prior to arrival |
| PVC | premature ventricular contraction |
| R | right |
| RA | right arm |
| RBC | red blood cell |
| (rbc) | red blood count |
| REG | regular |
| RESP | respirations, respiratory |
| RHY | rhythm |
| RL | right leg |
| RL | Ringer's lactate |
| RLQ | right lower quadrant |
| R/O | rule out |
| ROM | range of motion |
| RR | respiratory rate |
| RUL | right upper lobe |
| RUQ | right upper quadrant |
| Rx | prescription, therapy, treatment |
| S-A | sinoatrial |
| SAMPLE | signs & symptoms, allergies, medications, pertinent past Hx, last meal, events |
| Sa02 | arterial oxygen saturation |
| SC, SQ | subcutaneous |
| SE | common toxic side effects |
| SLUDGE | salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, gastrointestinal distress, emesis |
| SL | sublingual |
| SOAPE | Charting guidelines - subjective, objective, assessment, plan, evaluation |
| SOB | short of breath |
| Sp0202 | saturation via pulse oximetry |
| S/S | signs & symptoms |
| S/Sx | signs & symptoms |
| stat | immediately |
| SSN | social security number |
| STD | sexually transmitted disease |
| SW | stab wound |
| Sx | symptoms |
| Sz | seizure |
| T | temperature |
| TB | tuberculosis |
| TCA | tricyclic antidepressant |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| tid | three times a day |
| TIPS | trauma, infection, psychiatric, shock |
| TKO | to keep open (30 - 60 µgtt/min) |
| TPR | temperature, pulse, and respiration |
| TX | therapy |
| U | unit |
| UA | urinalysis |
| URI | upper respiratory infection |
| UTI | urinary tract infection |
| UV | umbilical vein |
| V-Fib, VF | ventricular fibrillation |
| VS | vital signs |
| V-Tach | tachventricular tachycardia |
| VT | ventricular tachycardia |
| w/ | with |
| w/o | without |
| WBC | white blood cell |
| WNL | within normal limits |
| WPW | Wolff-Parkinson-White (syndrome) |
| wt | weight |
| y/o, y.o. | years old |
| X | times |